BIO 102: General Biology II
Welcome to Biology 102
BIO 102 explores the diversity of plant life — from the simplest algae to complex flowering plants — and covers plant morphology, classification, and their role in the ecosystem.
Course Outline
UNIT I: INTRODUCTION
- The study of plants: Scope and Importance
- Why we study plants
- Variation and Classification in Biology
- Nomenclature and hierarchic relationships of organisms
- Classification of the plant kingdom
UNIT II: THE LOWER PLANTS
-
Thallophyta – Algae:
- General characteristics
- Types of thallus forms:
- Unicellular: Chlamydomonas
- Colonial: Pandorina, Volvox
- Filamentous: Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Oedogonium, Cladophora, Stigeoclonium
- Complex: Fucus
- Reproduction: vegetative and sexual
- Economic importance
-
Fungi:
- Types of thallus form:
- Unicellular: Bakers'/Brewers' Yeast
- Filamentous: Rhizopus stolonifer
- Complex: Mushrooms, Toadstools, Puffballs
- Importance to terrestrial ecosystems
- Reproduction: vegetative and sexual
- Types of thallus form:
-
Bryophyta:
- Thalloid liverworts: Marchantia – anatomy and reproduction
- Leafy liverworts: Porella – description and reproduction
- Mosses: Bryum coronatum – vegetative and sexual reproduction
UNIT III: THE HIGHER PLANTS
-
Pteridophyta:
- Introduction and significance
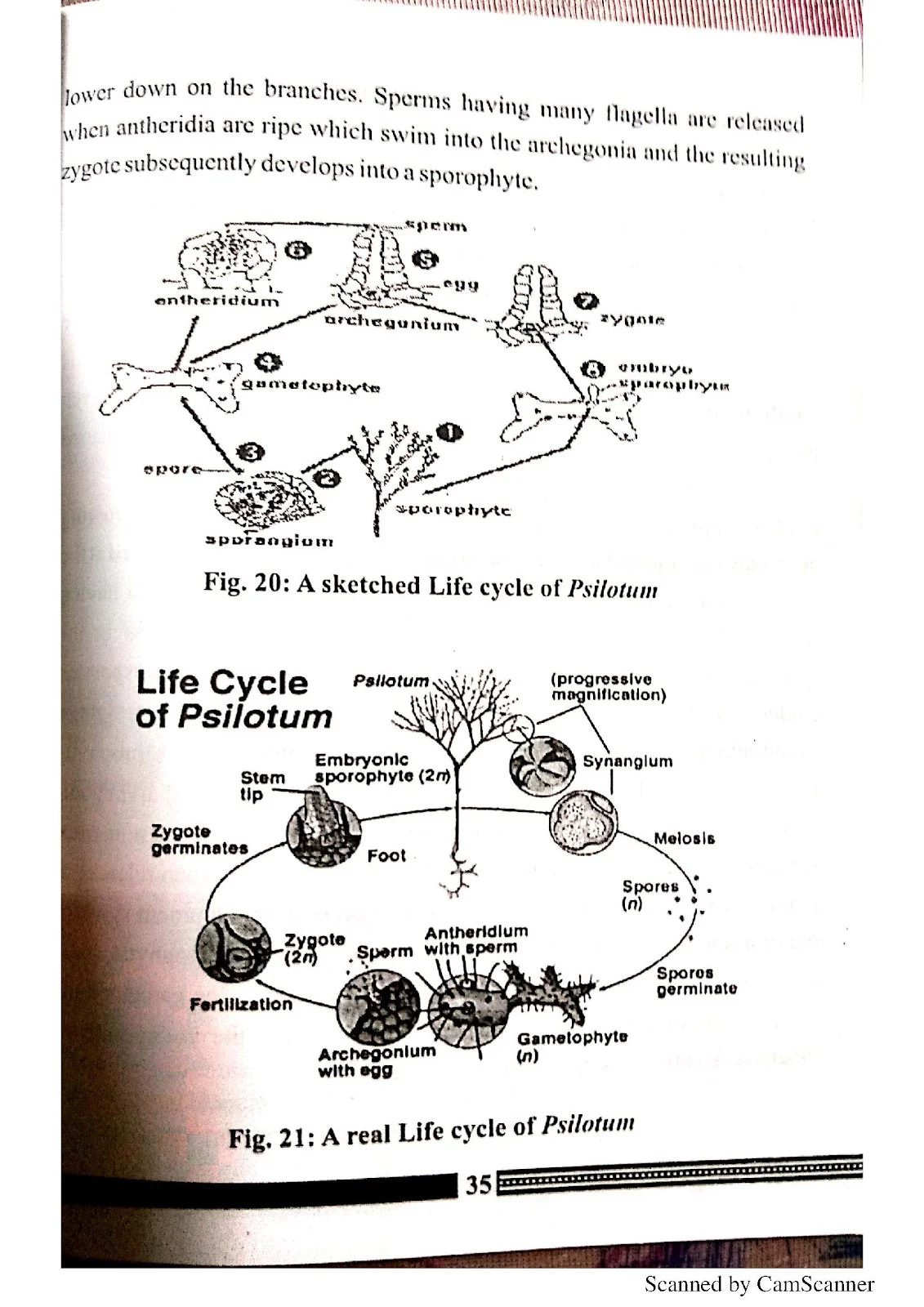
- Psilotum (Psilotinate)
- Lycopodium and Selaginella (Lycopodinae)
- Horsetails (Equisetinae)
- Ferns (Filicinae)
-
Spermatophyta:
- Gymnosperms (open seeds): adaptations and ecology
- Angiosperms (enclosed seeds): adaptations and ecology
UNIT IV: PLANT MORPHOLOGY
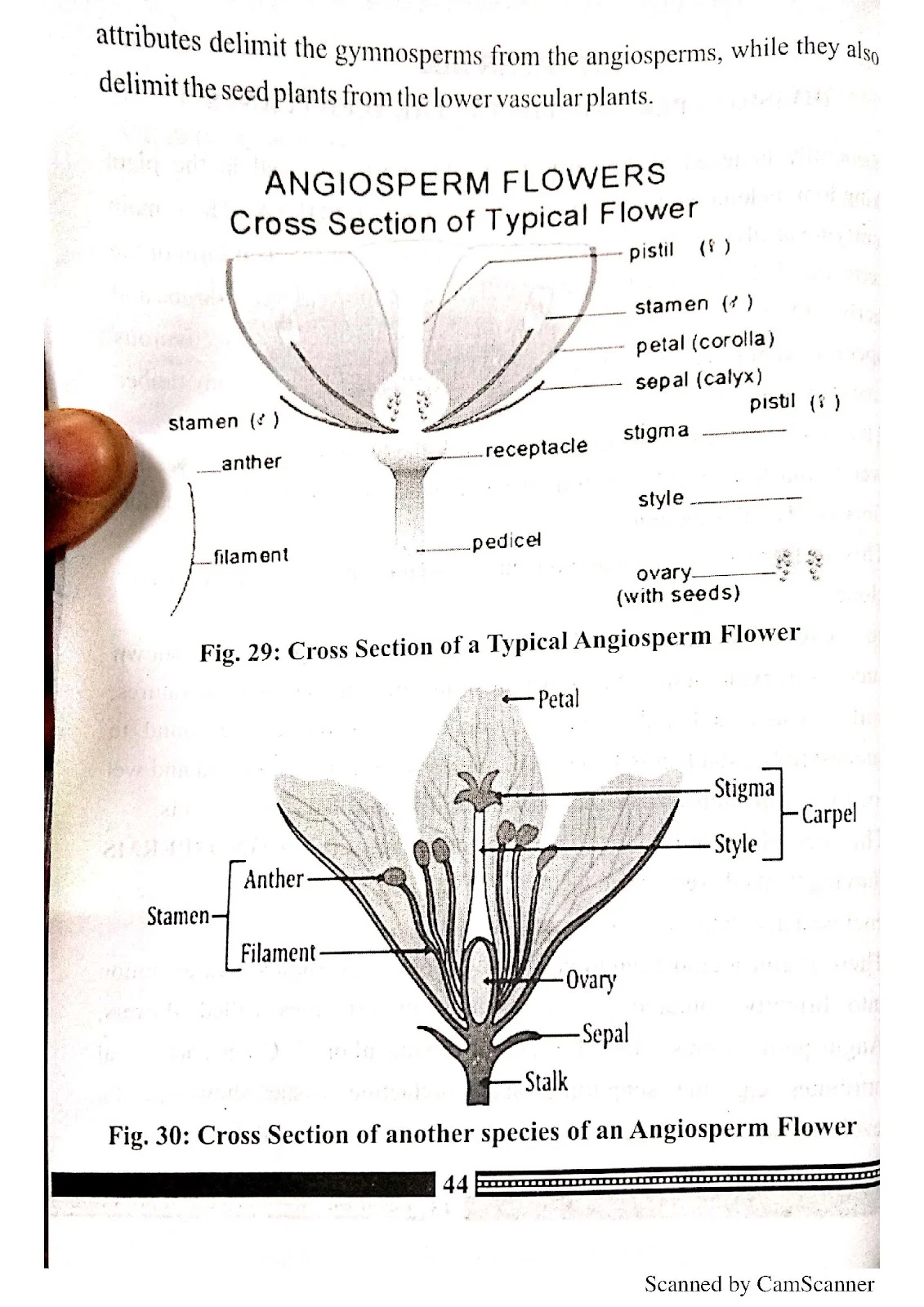
- Parts of flowering plants
- Morphology of Angiosperms – root and stem
- Leaf and flower arrangements
- Fruit morphology
Appendix
- Additional notes and diagrams relevant to lab and field practice










































































0 Comments