BIO 102: General Biology II
Welcome to Biology 102
BIO 102 explores the diversity of both plant and animal life. This section highlights animal diversity, their classification, structural features, evolutionary traits, and significance in the ecosystem.
Course Outline – Animal Diversity
UNIT I: INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL DIVERSITY
- Definition of Zoology and Animal Diversity
- Importance of studying animals
- Major characteristics of animals
- Basic classification of animals (Invertebrates vs. Vertebrates)
- Evolutionary relationships (Phylogeny)
- Symmetry in animals (Radial, Bilateral, Asymmetry)
- Levels of organization (Cellular, Tissue, Organ, System)
UNIT II: PROTOZOA & SIMPLE METAZOANS
- Phylum Protozoa: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena; nutrition, reproduction, locomotion
- Phylum Porifera (Sponges): Body structure, canal system, reproduction
- Phylum Coelenterata: Polyp & medusa forms, Obelia life cycle, coral reefs
UNIT III: WORMS AND PARASITES
- Phylum Platyhelminthes: Planaria, Tapeworm, Liver fluke, parasitic features
- Phylum Nematoda: Roundworms, Ascariasis
- Phylum Annelida: Earthworm anatomy, locomotion, reproduction
UNIT IV: ARTHROPODS, MOLLUSCS & ECHINODERMS
- Phylum Arthropoda: Insects, Crustaceans, Arachnids, examples like cockroach, mosquito, crab
- Phylum Mollusca: Mantle, foot, radula; examples: snail, octopus, Pila
- Phylum Echinodermata: Water vascular system; examples: starfish, sea cucumber
UNIT V: CHORDATES & VERTEBRATES
- Phylum Chordata: Notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail
- Sub-phylum Vertebrata:
- Pisces – Cartilaginous vs. bony fishes
- Amphibians – Frogs and metamorphosis
- Reptiles – Lizards and snakes
- Aves – Birds and flight adaptations
- Mammals – Humans and placental development
Appendix
- Flashcards, diagrams, and quiz questions for each phylum
- Tips: Storytelling, teaching method, and animal-phyla games for memory retention






































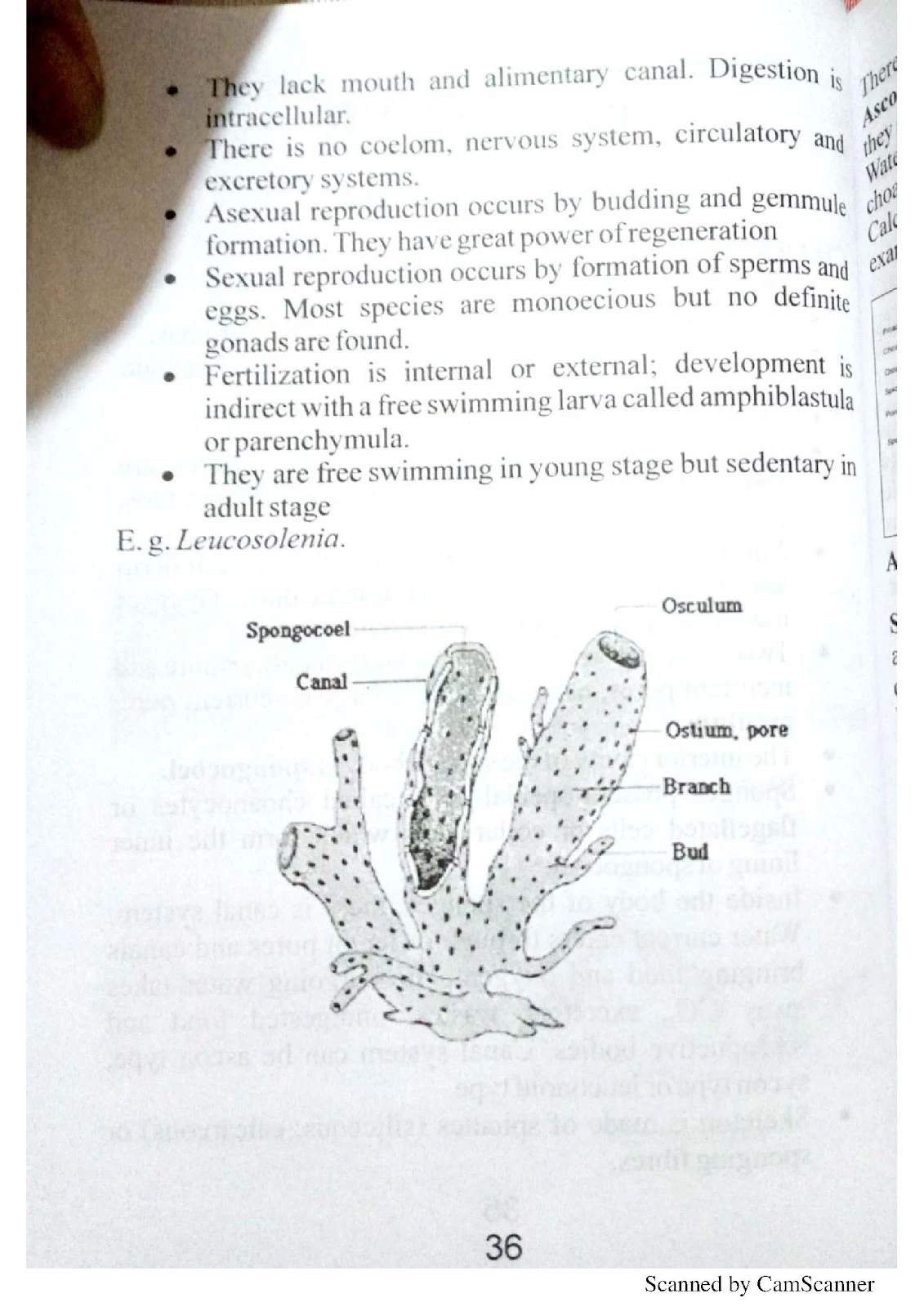
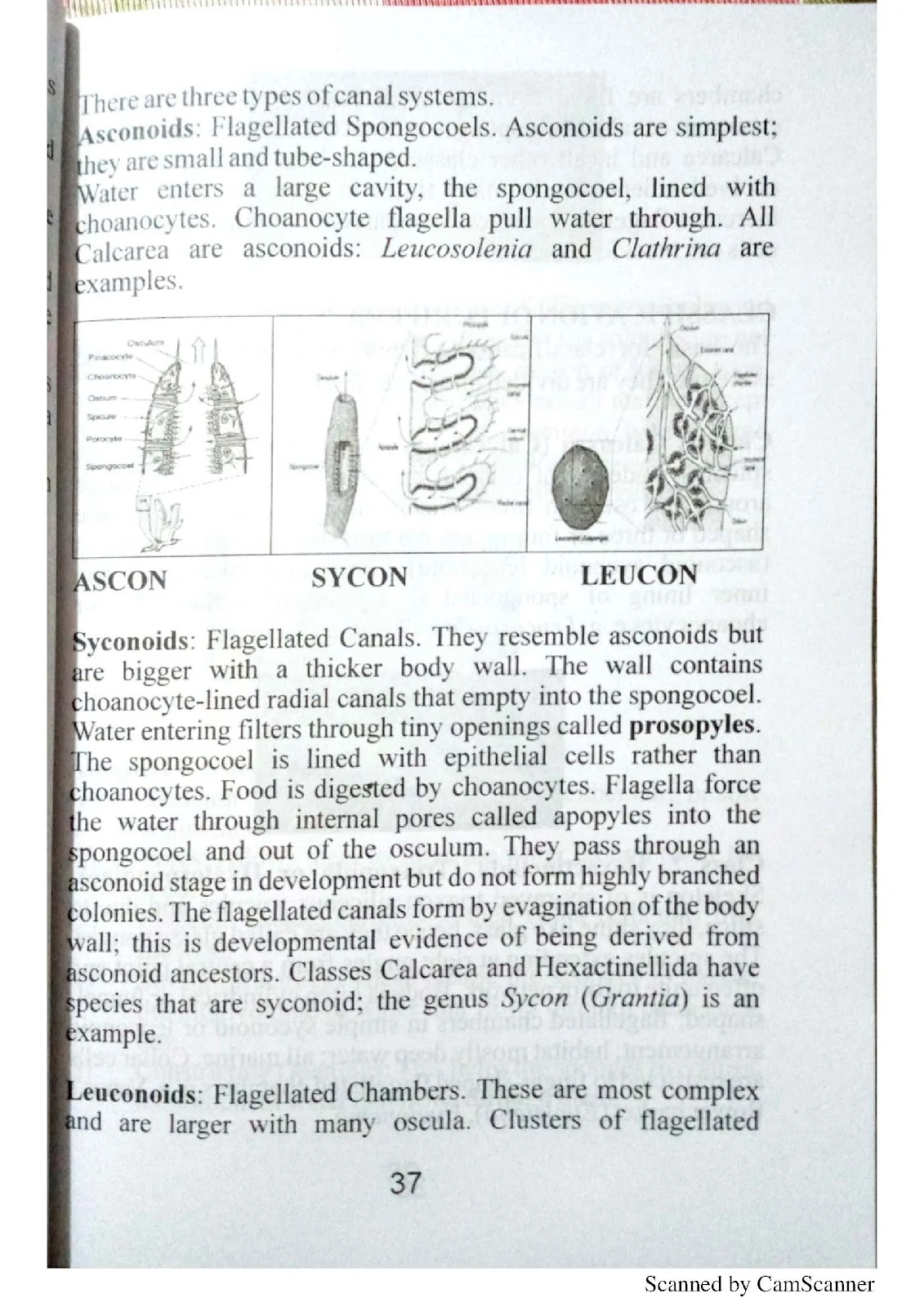
























































































































































0 Comments